Vitiligo is a common acquired depigmentation disorder characterized by the loss or reduction of melanocyte function in the skin, leading to localized or widespread white patches. Below is an overview of vitiligo:
Key Features of Vitiligo
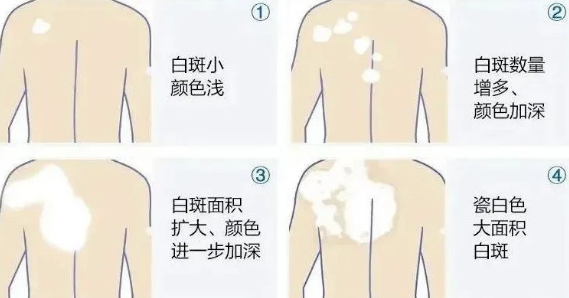
- Appearance:
- White patches on the skin with well-defined edges and a smooth surface.
- The affected areas may be more sensitive to sunlight and prone to sunburn.
- Distribution:
- Common on exposed areas like the face, neck, hands, and limbs.
- Can also occur on mucous membranes (e.g., mouth, nose) or the scalp.
- Painless Symptoms:
- Typically, the patches are not painful or itchy but may affect the patient’s appearance and psychological well-being.
Causes and Mechanisms
The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it may involve the following factors:
- Autoimmune Factors:
- The immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, leading to pigment loss.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Individuals with a family history of vitiligo are at higher risk.
- Environmental Triggers:
- Sun exposure, stress, or chemical exposure may trigger or worsen the condition.
- Oxidative Stress:
- Oxidative damage to melanocytes impairs pigment production.
- Neurochemical Factors:
- Localized nerve dysfunction may contribute to melanocyte abnormalities.
Classification of Vitiligo
- Localized Type: Patches are confined to a specific area of the body.
- Generalized Type: Widely distributed patches, often symmetrically arranged.
- Universal Type: Extensive depigmentation affecting most of the body surface.
- Segmental Type: Patches follow the distribution of a single nerve segment, often seen in young individuals.
Treatment Options
Vitiligo treatment is individualized and includes the following:
- Medication:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams and calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., tacrolimus).
- Oral Medications: Immune modulators and antioxidants.
- Phototherapy:
- Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) or excimer laser therapy promotes pigment production.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Melanocyte transplantation for stable cases.
- Traditional Medicine:
- Certain herbal remedies or acupuncture may benefit some patients.
- Psychological Support:
- Counseling or support therapy to address the psychological impact of vitiligo.
Precautions
- Avoid Triggers:
- Limit excessive sun exposure, manage stress, and avoid harmful chemicals.
- Balanced Diet:
- Include foods rich in vitamins C and E and essential minerals.
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Maintain good sleep habits, reduce stress, and boost immunity.