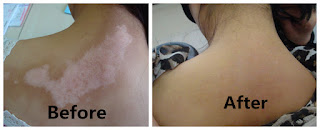
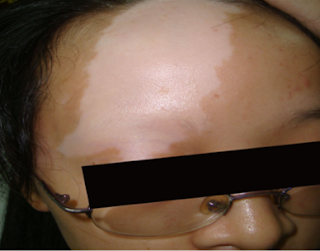
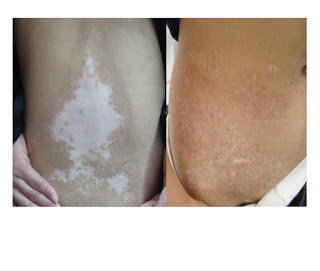
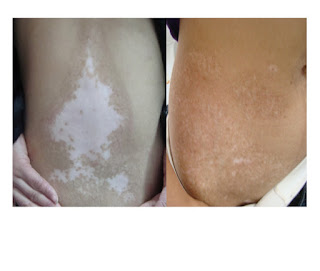
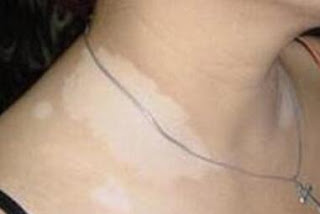
Vitiligo, a relatively common skin condition, is sometimes linked to hearing
loss, autoimmune diseases, or other disorders.
When a person has vitiligo, melanocytes are destroyed and blotches of white skin may appear on the body. Lack of melanocytes may even turn hair white in affected areas.
What causes Vitiligo?
There is no known cause of vitiligo, reports NIH. However, there is some speculation that it might be an autoimmune disease, which occurs when a person's immune system attacks some parts of their own body.
Some researchers believe that the melanocytes might be destroying themselves. Meanwhile, others think that vitiligo can be caused by a single event like a sunburn or emotional distress, although there is no evidence to prove this hypothesis.
What are symptoms of vitiligo
The main sign of vitiligo is pigment loss that produces milky-white patches (depigmentation) on your skin. Other less common signs may include:
Premature whitening or graying of the hair on your scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard
Loss of color in the tissues that line the inside of your mouth (mucous membranes)
Loss or change in color of the inner layer of your eye (retina)
Although any part of your body may be affected by vitiligo, depigmentation usually first develops on sun-exposed areas of your skin, such as your hands, feet, arms, face and lips. Vitiligo generally appears in one of three patterns:
Focal. Depigmentation is limited to one or a few areas of your body.
Segmental. Loss of skin color occurs on only one side of your body.
Generalized. Pigment loss is widespread across many parts your body.
When a person has vitiligo, melanocytes are destroyed and blotches of white skin may appear on the body. Lack of melanocytes may even turn hair white in affected areas.
What causes Vitiligo?
There is no known cause of vitiligo, reports NIH. However, there is some speculation that it might be an autoimmune disease, which occurs when a person's immune system attacks some parts of their own body.
Some researchers believe that the melanocytes might be destroying themselves. Meanwhile, others think that vitiligo can be caused by a single event like a sunburn or emotional distress, although there is no evidence to prove this hypothesis.
What are symptoms of vitiligo
The main sign of vitiligo is pigment loss that produces milky-white patches (depigmentation) on your skin. Other less common signs may include:
Premature whitening or graying of the hair on your scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard
Loss of color in the tissues that line the inside of your mouth (mucous membranes)
Loss or change in color of the inner layer of your eye (retina)
Although any part of your body may be affected by vitiligo, depigmentation usually first develops on sun-exposed areas of your skin, such as your hands, feet, arms, face and lips. Vitiligo generally appears in one of three patterns:
Focal. Depigmentation is limited to one or a few areas of your body.
Segmental. Loss of skin color occurs on only one side of your body.
Generalized. Pigment loss is widespread across many parts your body.